Population genetics(pop-gen):
Study of how population of a species change genetically over time leading to evolution
Group of individuals of a species that can interbreed is called population
Allele frequency:
How often certain alleles turn up in a population.
There are 5 factors which change this
1.Natural selection:
Alleles for fitter organisms become more frequent.
2.Sexual selection:
Alleles for more sexually attractive organisms become more frequent
3.Mutation:
New alleles popping up due to mistakes in DNA copying
4.Genetic drift:
Changes in allele frequency due to random chance
More impactful in small populations
5.Gene flow:
Changes in allele frequency due to mixing with new genetically different populations
More impactful in smaller populations
Hardey-Weinberg principal:
Frequency of alleles remains constant in a population from generation to generation giving that there is:
- No natural selection
- No sexual selection
- No mutation
- Huge population
- No gene flow
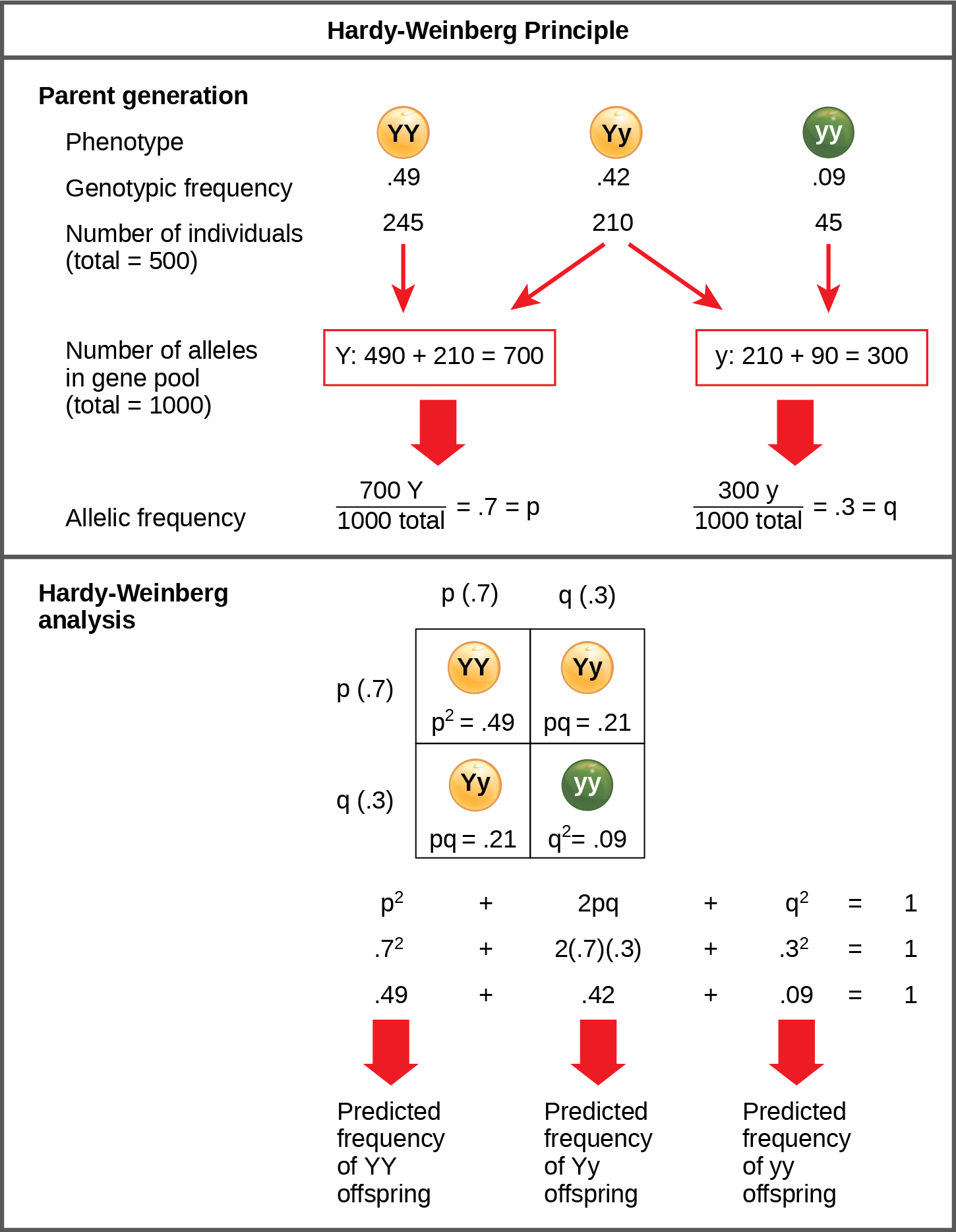
For mendelian traits,
Let the frequency of a dominant allele be p and the recessive allele be q,
p+q = 1 and p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
p^2 gives the frequency of homozygous dominant
2pq gives the frequency of heterozygous dominant
q^2 gives the frequency of recessive




